Views: 0 Author: JUSH Marketing Department Publish Time: 2025-12-17 Origin: Shanghai JUSH Pump








In the field of complex fluid transportation in industrial production, rotary lobe pumps, with their unique volumetric conveying principle, are gradually becoming the preferred equipment for conveying high-viscosity, particulate, and shear-sensitive media. However, inefficiencies, equipment wear and even production accidents caused by improper selection are still pain points faced by many enterprises. This article will systematically disassemble the core logic of rotary pump selection, from key parameter analysis, international standard application, eight-step selection process, to four major industry practical cases and five pit avoidance guidelines, to provide you with a set of practical selection methodologies that can be implemented.
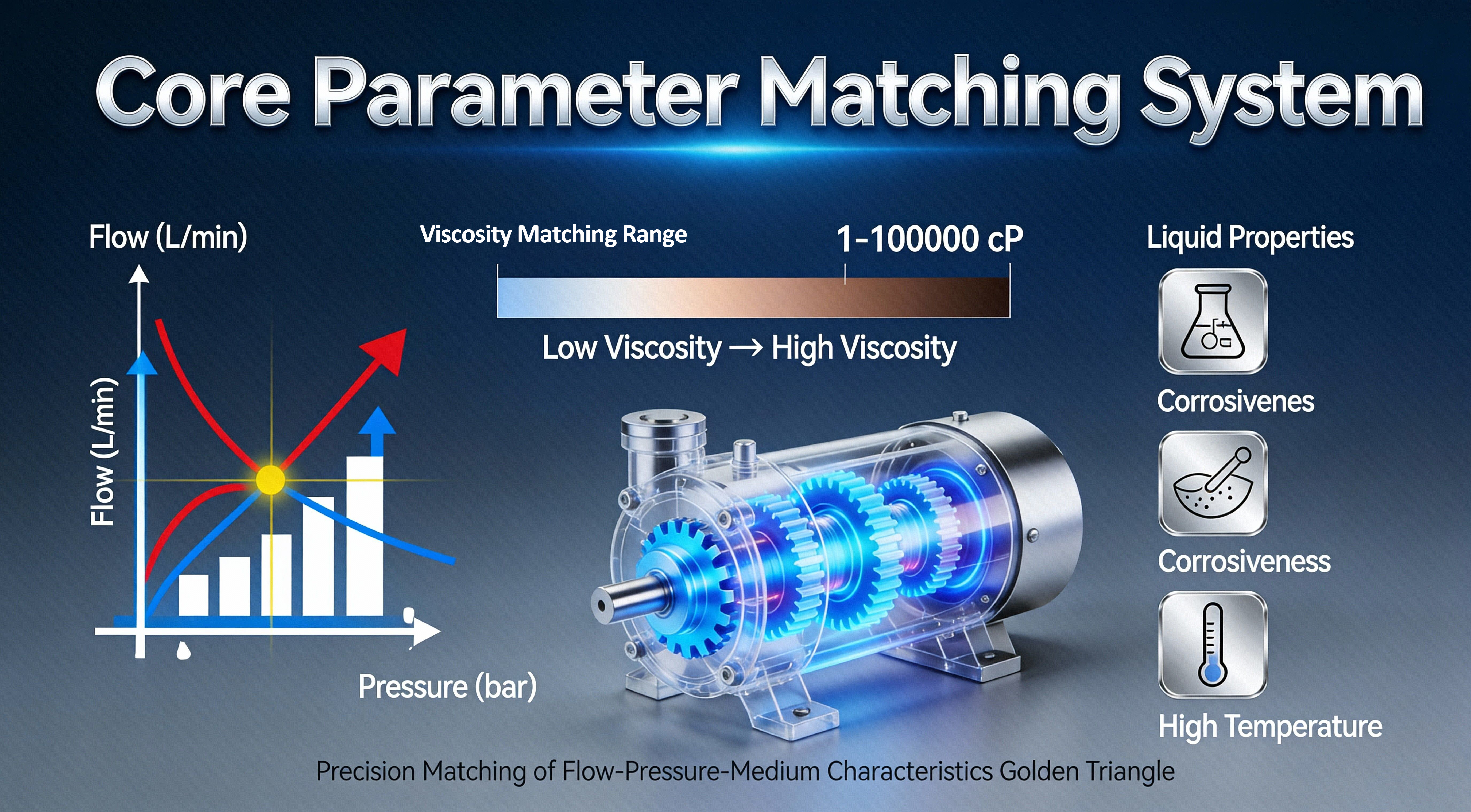
01. Core parameters for rotary pump selection: a comprehensive consideration from flow rate to viscosity.
Dynamic matching of flow rate and pressure is the primary step in pump selection. The flow rate (Q) of a rotary pump is typically expressed in cubic meters per hour (m³/h) or liters per minute (L/min) and must be accurately calculated based on the actual production cycle. For example, when a food processing plant transfers tomato paste with a viscosity of approximately 8,000 cP, and the filling line operates at 50 bottles per minute with a filling volume of 200 mL per bottle, the theoretical required flow rate is about 6 m³/h. In practical pump selection, an additional safety margin of 10%–20% should be reserved to accommodate operating fluctuations and system losses.
The determination of head (H) or operating pressure (P) must take into account multiple factors, including pipeline friction losses, vertical lifting height, and overall system back pressure. In a refinery
The viscosity compatibility range directly determines the selection of pump type. Rotary pumps offer significantly superior viscosity-handling capability compared to centrifugal pumps, typically covering a wide range from as low as 1 cP (e.g., water) up to 1,000,000 cP (e.g., molten plastics). For instance, in a seaweed processing plant in Qingdao, seaweed slurry with a viscosity of approximately 50,000 cP was initially conveyed using a centrifugal pump, resulting in insufficient flow performance. After replacing it with a lobe rotary pump, overall operating efficiency increased by about 40%.
It is also important to note that viscosity is highly temperature-dependent. For example, honey has a viscosity of approximately 7,000 cP at 20°C, which can be reduced to around 1,000 cP when heated to 60°C. Therefore, during pump selection, the actual fluid viscosity under real operating temperature conditions must be clearly defined to ensure accurate and reliable equipment matching.
Fluid characteristics are the key basis for material selection. When the solids content exceeds 5% or the particle size is larger than 3 mm, wear-resistant rotor materials such as high-chromium cast iron or duplex stainless steel should be selected. In pharmaceutical applications, such as transferring vaccine bulk solution, the pump’s wetted parts are typically manufactured from 316L stainless steel with an electropolished inner surface (Ra ≤ 0.4 μm) to meet the requirements of FDA 21 CFR Part 177.
In a chemical plant in Anhui Province, wastewater containing approximately 10% sulfuric acid was conveyed using a pump made of standard stainless steel. Due to insufficient consideration of material compatibility, the pump casing suffered corrosion and leakage within three months of operation. After replacing the wetted components with titanium alloy, the service life was extended to approximately two years.
2. Industry Standards Interpretation: From Domestic Regulations to International Certification
GB/T 44045-2024, the latest national standard for rotary pumps used in China’s petroleum and petrochemical industry, officially came into effect on December 1, 2024, replacing several previously fragmented standards. This standard clearly specifies the technical requirements for various pump types, including gear pumps, screw pumps, and lobe pumps.
According to the performance testing methods outlined in Annex A, the allowable flow rate deviation shall not exceed ±5%, the head deviation shall be within ±3%, and the seal leakage rate shall be limited to no more than 5 mL/h. Of particular note, Clause 6.4 of the standard mandates the use of dual mechanical seals for sealing systems. This requirement has already become a compulsory acceptance criterion in crude oil transfer pump retrofit projects at North China oilfields.
ISO 14847:1999 provides a more general and internationally applicable framework for the technical requirements of rotary positive displacement pumps. Chapter 5, titled “Applicability,” emphasizes that pump design shall take into account operating conditions such as ambient temperature (–20°C to 40°C) and installation altitude (≤ 1,000 m above sea level).
After obtaining certification in accordance with this standard, the Tornado® T1 series lobe pumps manufactured by the German company NETZSCH achieved a 15% increase in market share within European food processing plants. In China, organizations such as the Hefei General Machinery Research Institute have participated in the revision of this standard, enabling GB/T 44045-2024 to achieve over 90% compatibility with international standards.
Hygienic certification is a mandatory market entry requirement for the food and pharmaceutical industries. The 3-A Sanitary Standards require that all product-contact surfaces have a surface roughness of no more than 0.8 μm and adopt a crevice-free design to eliminate dead zones. EHEDG certification, on the other hand, verifies cleanability through EL-class testing.
Sanitary rotary lobe pumps manufactured by SHANGHAI JUSH Pump Co., Ltd. have successfully obtained both certifications. Thanks to their bi-wing lobe rotor design, shear forces are reduced by approximately 30%. In a yogurt processing plant application, this design improvement increased probiotic survival rates from 82% to 95%, demonstrating excellent performance in shear-sensitive product handling.
3. Eight step selection method: systematized decision-making process
The operating conditions data sheet must comprehensively document all critical parameters.
In one municipal sludge treatment project undertaken by an environmental engineering company, the initial pump selection failed due to the omission of an extreme operating condition in which the solids content increased from 20% to 35%, resulting in frequent clogging of the originally selected progressive cavity pump.
A standardized operating conditions data sheet should include the following core information: fluid name (including both common and chemical names), maximum / normal / minimum flow rates, suction pressure, discharge pressure, operating temperature range, viscosity (at 25°C and at actual operating temperature), solids content and particle size, corrosion classification, hygienic requirements, and a total of 12 essential technical parameters to ensure accurate and reliable pump selection.
Step 2: Preliminary Pump Type Selection Based on Fluid Characteristics
The initial selection of pump type should be based on the specific properties of the conveyed medium. For high-viscosity fluids (> 1,000 cP), lobe pumps or screw pumps are generally preferred. Media containing fibers (such as paper mill black liquor) are better handled by flexible impeller pumps. In hygienic applications, pump options are typically limited to lobe pumps or twin-screw pumps to meet strict sanitary requirements.
In a chocolate processing plant in Zhejiang Province, where the product viscosity reached approximately 60,000 cP, this selection step led to the elimination of gear pumps. The final solution was a jacketed rotary lobe pump with thermal insulation, effectively preventing chocolate solidification and blockage during operation.
Step 3: Material matching requires reference to corrosion manuals.
316L stainless steel is suitable for mildly corrosive environments with pH 4-10; Hastelloy C276 can withstand concentrated hydrochloric acid; PTFE coating is suitable for strong oxidizing media. A pesticide factory in Jiangsu province used a Hastelloy pump body to transport glyphosate mother liquor (pH 2-3, containing chlorine), and the service life was three times longer than that of 316L stainless steel.
Step 4: Performance curve verification is crucial to avoid "over-engineering an undersized vehicle."
Plot the calculated operating points (Qe, He) on the performance curve provided by the manufacturer, ensuring they fall within the high-efficiency zone (efficiency ≥ 75%). A chemical plant in Shandong failed to perform this step during model selection, resulting in an actual operating efficiency of only 52%, leading to chronic motor overload. After replacing the motor with a more compatible model, annual electricity savings of 120,000 kWh were achieved.
Step 5: Rotation speed optimization affects shear and wear.
High-viscosity media should use low rotation speeds (e.g., 300 rpm). In one cosmetics factory, when conveying face cream (viscosity 100,000 cP), reducing the rotation speed from 600 rpm to 200 rpm reduced the standard deviation of the product's particle size distribution from 15 μm to 8 μm. For media containing particles, the linear velocity needs to be controlled to ≤8 m/s to reduce wear.
Step 6: The design of the sealing system needs to consider multiple factors.
Single-end mechanical seals are suitable for ordinary working conditions; double-end seals with flushing systems are used for toxic media; magnetic seals achieve zero leakage. A chemical plant in Hebei Province uses API 682 standard double-end seals with Plan 53A flushing when transporting acrylonitrile (highly toxic), and the annual leakage is controlled below 0.5 L.
Step 7: The choice of installation method must be considered in conjunction with space conditions.
Horizontal installation is convenient for maintenance and suitable for spacious pump rooms; vertical installation saves 40% of floor space. After a ship selected a vertical cam pump, the space utilization rate was significantly improved. It is worth noting that vertical pumps have higher requirements for foundation rigidity and vibration analysis is necessary.
Step 8: Cost accounting should focus on the entire life cycle.
A car factory initially chose a domestically produced gear pump (120,000 yuan) due to its price, but the average annual maintenance cost reached 50,000 yuan. Later, they switched to an imported twin-screw pump (350,000 yuan), reducing the average annual maintenance cost to 12,000 yuan, resulting in a lower total cost over three years. The cost accounting should include: purchase price, energy consumption, spare parts, maintenance labor, and downtime losses.
04. Multi-Industry Application Cases: Scenario-Based Selection Strategy
The core requirements of the food industry are hygiene and low shear. A jam factory in Shanghai uses a 316L stainless steel rotary lobe pump to transport strawberry jam (containing 8 mm fruit pulp particles). The rotor features a special tooth design to ensure a fruit pulp integrity rate of ≥95%. This pump uses CIP (Clean-In-Place) online cleaning, reducing the cleaning time from 2 hours to 30 minutes per cleaning cycle, meeting the requirements of GB 12695-2016 for food contact materials.
The pharmaceutical industry has stringent requirements for sterility and precision. A vaccine factory in Beijing uses a rotary lobe pump with SIP (Self-Installation Injection) function to transport inactivated vaccines. The sealing system uses EPDM material, which can withstand 134℃ steam sterilization. Its flow control accuracy reaches ±0.5%, ensuring that the deviation of active ingredient in each batch of vaccine is ≤2%, meeting the requirements of GMP Appendix 1 for sterile pharmaceuticals.
The key to the environmental protection industry is anti-clogging and wear resistance. A wastewater treatment plant in Shenzhen used a cutting-type cam rotor pump to treat sand-containing sludge (25% solids content, particle diameter 2-5 mm). A pre-crushing device pulverized large particles to below 1 mm. The pump operated for 18 months without clogging, extending the maintenance cycle by five times compared to the original screw pump.
In the chemical industry, corrosion resistance and stability are paramount. A dye factory in Liaoning used a Hastelloy C276 pump to transport anthraquinone solution (temperature 120℃, pH 13), with a metal bellows mechanical seal. It operated continuously for 8000 hours without failure, far exceeding the contractually agreed 6000 hours.
05. Common Selection Mistakes and Avoidance Guidelines
Mistake 1: Selecting a pump based solely on flow rate. A paint factory, when transporting latex paint (viscosity 5000 cP), selected a pump model based solely on a flow rate of 20 m³/h, ignoring the effect of viscosity, resulting in an actual flow rate of only 12 m³/h. The correct approach is to request performance correction curves for different viscosities from the manufacturer, or directly provide a viscosity-flow rate conversion table.
Mistake 2: Ignoring gas-liquid mixed transport conditions. In oilfields, when transporting associated gas and liquid, if the gas content exceeds 10%, a special rotary pump with gas-liquid separation function is required. An oilfield in Xinjiang initially failed to consider this factor, leading to frequent pump cavitation. After replacing it with a screw pump with a buffer chamber, the operation stabilized.
Mistake 3: Overly pursuing imported brands. A brewery, when transporting malt extract, quoted 800,000 yuan for an imported pump, while a domestic sanitary cam pump (350,000 yuan) was EHEDG certified, and its performance was identical after 3 years of actual operation. For non-extreme operating conditions, it is recommended to prioritize domestic brands with equivalent certifications.
**Misconception 4:** Inappropriate sealing method selection. A chemical plant using a standard mechanical seal for transporting high-temperature heat transfer oil (300℃) experienced frequent leaks. Replacing it with a metal bellows seal and adding a quench system extended the seal life from 1 month to 12 months.
**Misconception 5:** Ignoring installation and maintenance space. A workshop using a compact pump due to limited space required disassembling the entire pipeline and shutting down the pump for 8 hours when replacing the mechanical seal. A reasonable installation spacing should meet the following requirements: ≥1.5 times the pump length before the pump, ≥0.8 meters to the pump side, and ≥1.2 meters above the pump.
Choosing a [Shanghai Jiushi] transfer pump is not just selecting a piece of efficient and reliable equipment—it is choosing a trustworthy partner for your process. We are committed to infusing every inch of your pipeline with dependable power, making every transfer more efficient and every production line more continuous. Contact us today for a tailored solution, and let us help propel your enterprise forward.